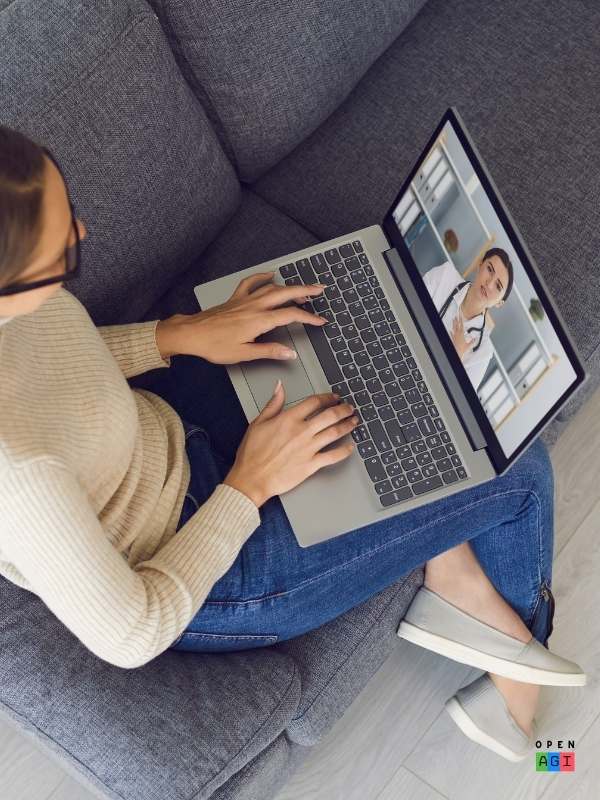
OpenAGI - Your Codes Reflect!






































































































































Intelligence into
the products,
Empowering enterprises to tailor AI, ML into their products. Crafting scalable, cost-efficient strategies built to last.
Open AGI
Re-imagining Enterprise with us
At our core, we are a research-driven organization
Steering AGI development
Empowers Enterprises and innovators with Advanced AI, ML and Generative AI
products with strong focus on Platform and Product Engineering combine deep research and evidence-based strategies and business integration to align technology with organizational goals.
The platform specializes in building domain-specific models, deploying intelligent agent systems, designing scalable distributed machine learning architectures for both Small Language Models (SLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs).
OPEN AGI
What We Do
Deliver AI Transformation from strategy to production - model development, agent-based orchestration, and distributed ML.
Build and optimize AI models tailored for specific business and technical domains.
Implement and manage rapid deployments using proven models, APIs, and Cloud Platforms.
End-to-end stage-by-stage journey from data preparation, training, and inference to production deployment and continuous improvement.
Design and deploy globally scalable machine learning solution with intelligent load balancing, containerization, fault tolerance and cloud agnostic environments across cloud and edge.
OpenAGI Philosophy
Transparency & Accountability in AI
A comprehensive framework for open, transparent, and accountable AI development, fully aligned with the Model Openness Framework (MOF) by LF AI & Data - Generative AI Commons.
Foundation & Transparency
Core transparency in training, data, and model artifacts
Safety & Governance
Risk evaluation, accountability structures, and bias mitigation
Operations & Accountability
Supply chain transparency, monitoring, and continuous improvement
Model Openness Framework (MOF) Classification
OpenAGI adopts the MOF tiered classification to ensure genuine openness and combat openwashing.
LF AI & Data - Generative AI Commons
Open Model
Minimum requirements for openness, including open weights and basic documentation.
Requirements
Open Tooling Model
Intermediate level ensuring the availability of tools to use and inspect the model.
Requirements
Open Science Model
Highest level of openness, enabling full reproducibility and independent verification.
Requirements
Core transparency in training, data, and model artifacts
Open Training Process
Full transparency in hyperparameters, optimization details, and architecture choices. Every decision in the training pipeline is documented and accessible, enabling reproducibility and community collaboration.
Open Datasets & Data Governance
Traceable data sources, preprocessing pipelines, and metadata. Includes privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), copyright compliance, data poisoning mitigations, and GDPR/CCPA adherence with opt-out mechanisms.
Open Weights & Model Artifacts
Model parameters available for inspection, modification, and deployment. Includes intermediate checkpoints, energy usage metrics (kWh, carbon footprint), infrastructure details, and sustainability tradeoffs documentation.
Risk evaluation, accountability structures, and bias mitigation
Safety & Risk Evaluation
Multi-dimensional safety metrics: robustness (adversarial inputs, distribution shifts), factuality (hallucination rates, TruthfulQA), toxicity propensity, jailbreak susceptibility, and out-of-scope use detection for responsible deployment.
Governance & Accountability
Shared responsibility models defining accountability at each level. CVE-style vulnerability disclosure (90-day windows), EU AI Act compliant incident reporting (15-day notifications), cross-functional governance committees, and audit trails for every model version.
Bias, Fairness & Stratification
Identification of biases across the lifecycle: Sample Bias (representative mismatch), Label Bias (systemic outcome errors), and Pipeline Bias (ingestion & feature engineering). Evaluation uses intervention-aware metrics (FPR/FDR for punitive; FNR/FOR for assistive) to ensure demographic parity.
Supply chain transparency, monitoring, and continuous improvement
Supply Chain Transparency
SPDX 3.0 standard AI & Dataset profiles with complete dependency tracking. Documents training data sources, evaluation data, licenses, security measures, and can be embedded in Open Container Initiative (OCI) artifacts for standardized AI model packaging.
Open Inference & Serving
Complete visibility into serving code, content filters, and routing logic. Open inference systems ensure transparency in how models process inputs and generate outputs, including safety mechanisms, optimization strategies, and third-party testing accreditation.
Continuous Monitoring & MLOps
Model drift detection, user feedback integration, update transparency, and longitudinal tracking. AI BOM versioning ensures every release is independently auditable with transparency scores tracked over time and documented weight changes.
Five Pillars of Transparent AI
A intuitive workflow ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the entire AI development lifecycle
Data Preparation
Generate data cards automatically; validate licenses; document preprocessing code
Click to see all 4 details
Training
Capture hyperparameters, architecture, intermediate checkpoints; auto-generate AI BOM profiles
Click to see all 4 details
Evaluation
Populate model cards with stratified metrics, safety results, known limitations
Click to see all 4 details
Packaging & Release
Bundle into Open Container Initiative (OCI) artifact; auto-sign with Sigstore; finalize AI BOM; verify license compliance
Click to see all 4 details
Deployment
Verify signatures; extract AI BOM for compliance checks; set up monitoring for drift
Click to see all 4 details
The OpenAGI philosophy represents a commitment to transparency, safety, and accountability in AI development. By opening every aspect of the AI lifecycle—from training and data governance to safety evaluation, bias mitigation, supply chain transparency, and continuous monitoring—we enable reproducibility, foster innovation, build trust, and ensure responsible AI deployment that serves all stakeholders equitably.
Do you want to build transparent, safe, and accountable AI?
Join usOpenAGI | Transparency Framework
Shaping the Future:
Enhancing Human Creativity, Promoting Ethical Intelligence, and Driving Transformative Change
We aim to empower individuals and organizations to consciously steer the evolution of Artificial Intelligence for the benefit of all.
We believe AI isn't just the future, it's a transformative edge for organization today, we envision to democratize advanced, responsible AI by making the tools, knowledge and methodologies, while upholding ethical and human-centric values at every step.
VISION
Our Vision
Enhancing Human Creativity through AI tools and technologies
Promoting Ethical Intelligence in all AI development
Driving Transformative Change across industries
Empowering organizations to steer AI evolution
Democratizing advanced, responsible AI technologies
MISSION
Democratize responsible AI: Make advanced, safe, and explainable AI technologies
We are committed to building AI systems that prioritize human welfare, ethical considerations, and sustainable development.
MISSION
Our Mission
Democratize responsible AI: Make advanced, safe, and explainable AI technologies
Embed fairness, transparency, and human-centric values in every algorithm, model, and dataset.
Support open research, multi-modal learning, and diverse perspectives in AGI development.
Build robust safeguards, continuous monitoring, and human-in-the-loop systems for trustworthy AI.
Inspire the next generation of conscious efforts to shape AGI that uplifts humanity, respects privacy, and sustains the planet.
PROBLEM
Navigating digital transformation, organizations face significant resistance and bureaucracy, hindering adoption of crucial innovations like cloud, low-code/no-code, and AI, thereby compromising agility and resilience.
Organizations struggle with complex challenges that prevent them from fully leveraging AI and digital transformation opportunities.
PROBLEM
Key Challenges
Bias Amplification, Ethical Lapses & Loss of Trust
Algorithmic Errors & Catastrophic Failures, Unintended Consequences, Lack of Explainability & Accountability, Reinforcing Silos & Complexity are paramount challenges in AI deployment.
Ecosystem Complexity
Arises from diverse, interconnected components, creating dynamic interactions, dependencies, and emergent behaviors challenging to manage and predict.
Bureaucratic Mountain
Impedes progress through rigid structures, convoluted processes, and entrenched resistance, stifling innovation, decision-making, and organizational evolution in dynamic environments.
Agility Requirements
Crucial for navigating today's turbulent markets, demanding agile adaptation, swift decision-making, and seamless execution to seize opportunities and mitigate evolving threats.
SOLUTION
AI transformation, from model development and agent orchestration to globally scalable ML deployments. Our research-driven, evidence-based approach ensures seamless integration, cost optimization, and continuous innovation.
We provide AI solutions that address the complex challenges organizations face in their digital transformation journey.
SOLUTION
Our Solutions
Enterprise AI
Create an AI layer to integrate models and NLP, enhancing product intelligence. This transformation enables businesses to leverage agentic systems and improve orchestration efficiency.
Approach
Utilize feature engineering and cost optimization frameworks, such as TCO analysis, to enhance performance and ROI while adopting product and platform engineering in a phased approach.
Strategy
Employs a dual-strategy approach combining Transformation A (optimizing current operations with AI) and Transformation B (creating new AI-driven business models).
Benefits
Each use case demonstrates measurable ROI through improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences while establishing foundation for next-generation business model innovation.
Stay Connected
OpenAGI News
Specializing in AI, ML, and GenAI products, with cutting-edge expertise in enterprise AI, infrastructure, and research. Stay connected with us to learn more on the latest trends and developments in the AI space.
What We Do
Enterprise AI
We deliver AI transformation through model development, intelligent agent systems, distributed ML architectures, and Small Language Models (SLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) implementation from strategy to production operations.
Build specialized AI models from scratch for domain-specific requirements with full control over architecture, training, and optimization
Deploy multi-agent orchestration with RAG, vector databases, and rapid deployment using proven models and cloud platforms
Design globally scalable ML architectures with intelligent load balancing, containerization, and fault tolerance across continents
Stage by Stage methodology from data preparation through production operations, training, inference, and continuous improvement
How We Do
Our Implementation Methodology
Strategic two-fold approach combining model development and intelligent agent systems with distributed ML architecture and systematic Small Language Models (SLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) implementation journey.
Model development for specialized domains OR intelligent agent orchestration with rapid deployment using proven models, APIs, and cloud platforms
Enterprise microservices that decouple model components, enabling independent global scaling from cloud to edge across multiple continents
Systematic approach: Foundation → Development → Inference → Deployment → Operations with continuous improvement and optimization
Global deployment with intelligent load balancing, model versioning, data drift monitoring, and fault tolerance across all regions
Discover Our AI Implementation Approach
Learn about our two-fold strategy covering model development, intelligent agent systems, and Small Language Models (SLMs) and Large Language Models (LLMs) implementation journey.
AI Innovation
Our Research-Driven Process
We co-create enterprise AI products through our systematic, research-centric approach that transforms your business approach.

Discovery & Analysis
We conduct analysis of your enterprise architecture, identify AI opportunities, and develop evidence-based strategies that align with your business objectives.
Prototype & Development
We build and deploy cutting-edge AI products using proven methodologies, advanced LLMOps, and innovative development frameworks tailored to your enterprise needs.


Deploy & Optimize
We launch your AI initiatives with performance-optimized deployment strategies, providing ongoing support and intelligent monitoring for maximum business impact.
Optimize Your Data for Better AI Performance
Unlock the full potential of your AI models with expert feature engineering. Improve accuracy, reduce costs, and accelerate deployment.
Total Cost of Ownership for Enterprise AI
A framework for calculating and optimizing the total cost of ownership of enterprise AI and SLM/LLM deployments across all phases from foundations to advanced optimization.
Phases in TCO Framework
Phase 1: TCO Foundations
* Time estimates are based on typical enterprise AI implementations and may vary based on organizational complexity, team size, and specific requirements.
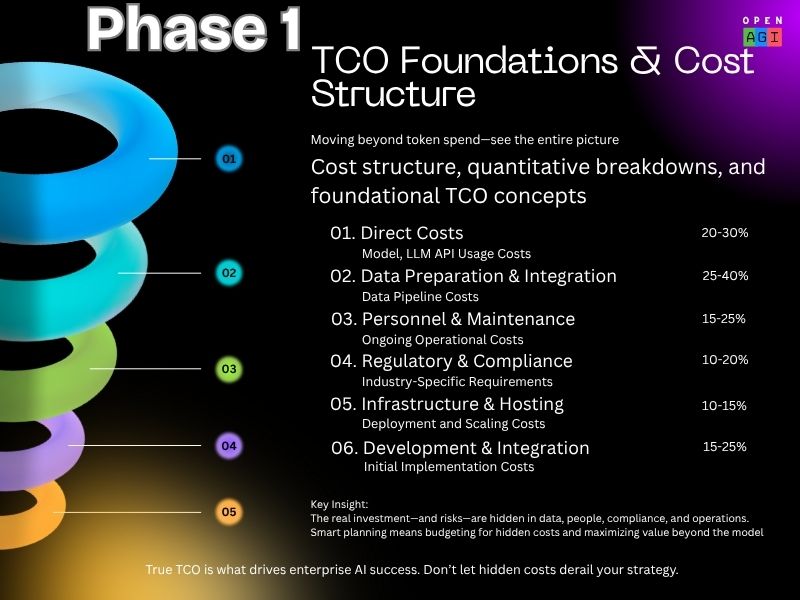
Identify all direct cost components: API usage, data prep, personnel, compliance, infrastructure, and integration. Quantify each precisely
Explore Phase DetailsReady to start your next AI project now?
Transform your organization with tailored AI, ML, and AI Infrastructure. Our expert panel delivers cost-effective, future-proof strategies.
Blog posts
Deep Dives
Our blog provides the deep dives on AI, ML, and GenAI.

Featured Post
New Year 2026: The Year of more Practical AI for Enterprise consumptionYear 2026! This year marks the rise of practical AI for enterprises—focused on real ROI, scalable automation, and transparency. Businesses will prioritize efficiency, responsible adoption, and integrating AI seamlessly into workflows for measurable, sustainable impact across industries.

Generative AI is revolutionizing the way we create and interact with language. From chatbots to content generation, it’s transforming how we communicate and access information.

Citizen developers are transforming business IT by creating and deploying applications without traditional development roles. This empowers organizations to innovate faster and respond to changing business needs.

AI transformation involves integrating AI into business processes to enhance efficiency, decision-making, and customer experience. This includes automating tasks, improving data analysis, and enabling real-time insights.
Explore new algorithms, conquer challenges, embrace learning from setbacks, and achieve creditable results in AI-driven decision-making. Collaborate, share knowledge, and empower citizen developers with essential AI skills to revolutionize your business products.
Make the most of the cloud. Let us help you adopt cloud-native architectures, optimize cloud resource consumption, ensure compliance and safety, and simplify complexity. By assimilating lessons from challenges, improving strategies, and adopting a cloud-centric mindset, organizations may grow and prepare for AI-driven digital transformation. How is our secret sauce determined?
Empowering budding citizen developers to build their own products without software development experience, dogfooding cutting-edge technology, experimenting, crawling, falling, failing, restarting, learning, mastering, sharing, and becoming self-sufficient, building a culture of innovation, driving digital transformation and embracing community-driven development.
Industry Research that is rewriting the AI landscape
A curated collection of ground-breaking research into Language model architectures, optimization, and safety that is actively shaping the frontier of Artificial General Intelligence.
Featured Research
Synthesized key findings from ground-breaking papers in the field.
Language Model
A deep dive into 70+ foundational papers covering optimization and scaling.
Exploration
Continuously updated collection of the latest advancements in AGI.
Ready to Transform Your Business with AI?
Take the first step towards AI transformation. Our approach ensures successful implementation and measurable results.
AI Transformation Journey
Step by Step Approach
The AI Transformation Journeys framework helps organizations understand and implement AI transformation through progressive stages, from initial experimentation to full-scale AI integration. It's not just about technology—it's about cultural change, continuous learning, and strategic alignment.
Foundation Phase
Building the groundwork for AI adoption through experimentation and strategic planning
Hello World Moment
Begin your AI journey by experimenting with APIs and testing Large Language Models (LLMs). Build simple applications using GPT, Claude, or other models, and explore frameworks like LangChain. This is your 'aha!' moment where AI becomes real and tangible.
Crawl with AI
Deepen your understanding of the AI ecosystem by exploring vector databases, prompt engineering, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and multimodal inputs. Begin forming a strategic roadmap for AI implementation.
Strategize with Tangible Outcomes
Transform curiosity into concrete results by building proof-of-concept projects aligned with your business goals. This stage bridges the gap between AI experimentation and practical business applications.
Get the Big Picture
Develop an understanding of how LLMs can impact various aspects of your organization, from customer service to knowledge management and analytics.
Walk with AI
Foster collaboration between technical and business teams to integrate AI into workflows. Establish governance rules, boundaries, and metrics for measuring impact.
Stand Up for the Future
Begin active implementation while addressing technical debt, organizational inertia, and skepticism. This stage focuses on overcoming challenges and building momentum.
Implementation Phase
Moving from strategy to active deployment and organizational integration
Transformation Phase
Scaling AI initiatives and embedding AI into organizational culture
Thrive in the AI Era
Transition from 'doing AI' to becoming AI-native. Scale projects, build AI-powered customer journeys, and enhance internal decision-making processes.
Transform Your Life
Embed AI into your organizational culture. Transform how teams think, build, and solve problems, creating value for employees, partners, and customers.
Iterate with AI
Implement continuous improvement through feedback loops. Refine models, processes, and strategies based on lessons learned and emerging best practices.
Keep the Momentum
Maintain progress through defined metrics, outcome monitoring, and strategic alignment. Focus on sustaining AI operations and continuous evolution.
Leap into the AI Era
Achieve full AI maturity where AI becomes your co-creator, insight engine, and value driver. Build innovative solutions that were previously impossible without AI.
AI-Driven Phase
Achieving full AI maturity and leading innovation in the AI era
Execution Excellence
Forward Deployed Engineering
A modern methodology focused on bridging the gap between complex engineering and tangible business impact.
Discovery & Value Stream Mapping
Mapping end-to-end processes to identify high-impact value streams and define technical success criteria.
Rapid Prototyping (MVP)
Accelerated development of Minimal Viable Prototypes to confirm ROI and validate technical feasibility.
Cloud-Native Scale-up
Deploying scalable Kubernetes architectures with integrated security guardrails, observability, and phased enterprise rollouts.
Optimization & Handoff
Continuous refinement via KPI monitoring and A/B testing, followed by structured handoffs with comprehensive runbooks.
Success Enablers
Frequent Customer Syncs
Ensures continuous alignment and early issue detection through proactive milestone reviews.
Deep SME Pairing
Integrating domain expertise directly into the development cycle for accurate knowledge capture.
Iterative Feedback Loops
Driving continuous improvement through rapid feedback cycles from end-users and stakeholders.
Metric-Driven Decisions
Using quantitative data to justify strategic expansion and prove the value of every deployment.
Enterprise AI
Reimagining Enterprise ecosystem
Building, deploying, and managing AI at Enterprise Scale
Foundation & Strategy
Establish your AI strategy and understand the landscape
Development & Engineering
Build robust AI applications with best practices
Begin with small, deliberate steps to build Enterprise AI capability.
Strategy
Start with AI Transformation and TCO analysis
Build
Develop with Spec-Driven Development
Deploy
Implement Vector Databases and RAG
Scale
Integrate with MCP and AI Agents
Are you interested in AI-Powered Products?
Get In Conversation With Us
We co-create enterprise AI architecture, develop cutting-edge agentic AI patterns, advance LLMOps methodologies, and engineer innovative testing frameworks for next-generation AI products with our research-centric approach.
Tippman Pl, Chantilly, VA
20152, USA
Timezone
Oakglade Crescent, Mississauga, ON
L5C 1X4, Canada


